Many people wonder about the financial contributions of the world's wealthiest individuals. It's a question that, you know, comes up quite a bit. There is a lot of public interest, actually, in how top earners manage their money. This includes, very much, how they handle their tax responsibilities.
The question "Does Elon Musk pay income tax?" is a popular one. It often sparks lively conversations, too. People are naturally curious about the finances of someone so prominent. They want to understand the system, in a way, that applies to very rich people.
This article will look into how income tax works for individuals like Elon Musk. We will explore the common ways billionaires receive income. We will also see how tax laws apply to their unique financial situations. It's a bit more complex than it might seem at first glance, you know?
Table of Contents
- Elon Musk: A Brief Overview
- Understanding Income for the Super Rich
- How Taxes Are Paid by Billionaires
- Public Perception Versus Tax Reality
- Frequently Asked Questions About Billionaire Taxes
Elon Musk: A Brief Overview
Elon Musk is a very well-known figure, really. He is famous for leading several innovative companies. These include Tesla and SpaceX, for example. He has also been involved with X (formerly Twitter) and Neuralink.
His work has had a big impact on many different industries. He has pushed boundaries in electric vehicles and space exploration. He is often seen as a visionary, you know, someone who sees the future.
His personal wealth has grown significantly over the years. This growth is mostly tied to the value of his company shares. It is a bit different from how most people earn money, actually.
Personal Details and Bio Data
| Full Name | Elon Reeve Musk |
| Date of Birth | June 28, 1971 |
| Place of Birth | Pretoria, Transvaal, South Africa |
| Citizenship | South Africa, Canada, United States |
| Primary Companies | Tesla, SpaceX, X (formerly Twitter), Neuralink, The Boring Company |
| Known For | Entrepreneurship, engineering, innovation, space exploration, electric vehicles, artificial intelligence |
Understanding Income for the Super Rich
When people ask, "Does Elon Musk pay income tax?", they are often thinking about traditional salaries. However, the financial lives of billionaires are usually quite different. Their wealth comes from various sources, you know, not just a regular paycheck.
Most of their money is tied up in assets. These assets are things like company shares or property. This is a very important distinction, actually, for tax purposes.
Salary vs. Stock Options
Many top executives, including Elon Musk, take a very low or even zero salary. For instance, reports often indicate that his Tesla salary is quite small, or even $1. This might seem strange, but there's a good reason for it, you know.
Their real compensation comes from stock options or grants. These are agreements that let them buy company shares at a specific, often very low, price. This happens later on, you know, at a future date.
These options are a huge incentive for them to grow the company's value. If the company does well, their options become much more valuable. It's a direct link, in a way, between their performance and their personal wealth.
The Role of Capital Gains
When someone sells an asset for more than they paid for it, that profit is called a capital gain. This applies to stocks, property, or other investments. It is a key way, too, that very wealthy people generate taxable income.
There are different tax rates for capital gains. If you hold an asset for less than a year, it's a short-term gain. This is taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, more or less. If you hold it longer than a year, it's a long-term gain. These have lower tax rates, which is a big benefit, you know, for long-term investors.
Billionaires often hold their assets for a very long time. This allows them to benefit from these lower long-term capital gains rates. It's a common strategy, in some respects, for managing tax obligations.
Unrealized Gains and Taxation
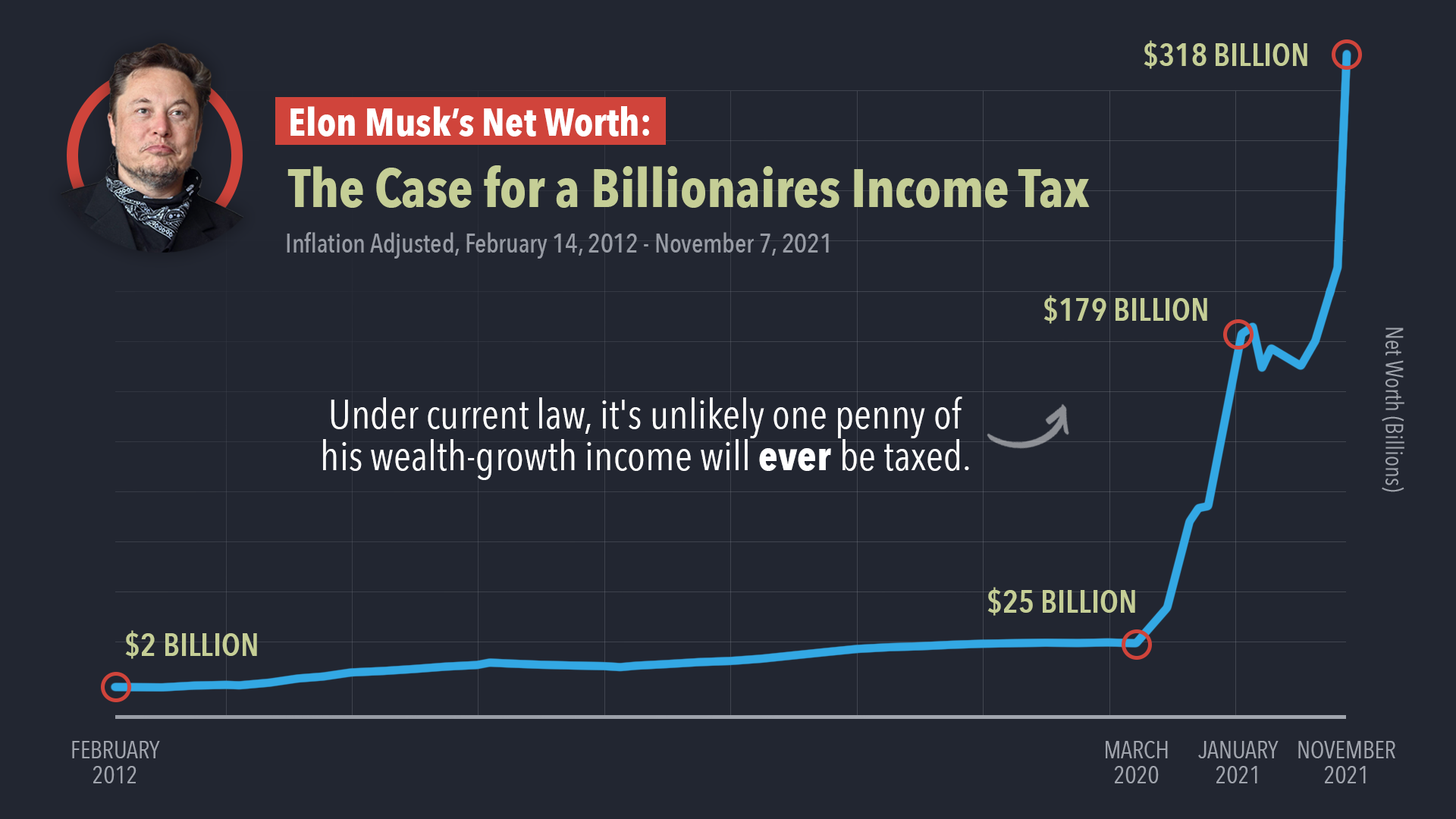
Here's a crucial point that often causes confusion. When the value of someone's stock goes up, but they haven't sold it yet, that's an "unrealized gain." It's like the money is there, on paper, but not in cash, you know?
These unrealized gains are not taxed. You only pay tax when you actually sell the asset and realize the profit. This is a fundamental principle of income tax law, actually, in many countries.
So, someone like Elon Musk could have billions of dollars in stock value. But if he hasn't sold those shares, he doesn't pay income tax on that increase in value. This is why, you know, people might have very high net worth but relatively low taxable income in a given year.
How Taxes Are Paid by Billionaires
Even if a billionaire doesn't take a large salary, they still pay taxes. This happens when they convert their assets into cash. There are specific events that trigger tax payments, you know, for them.
It's not that they avoid taxes completely. It's more about when and how those taxes become due. The system is set up, in a way, to tax realized income.
Exercising Stock Options and Taxes
When Elon Musk, for example, exercises stock options, he buys shares at a special price. The difference between that special price and the current market price is usually treated as income. This is a very common scenario for executives.
This "income" is then subject to ordinary income tax rates. He might then sell some of those shares to cover the tax bill. This is a typical way, you know, that these large tax payments occur for him and others in similar positions.
He famously sold a significant amount of Tesla stock in 2021. This was, in part, to cover a large tax bill related to exercising stock options. It was a very public event, too, that highlighted this aspect of billionaire taxation.
Charitable Contributions and Tax Benefits
Wealthy individuals often make large charitable donations. These donations can provide significant tax deductions. They reduce the amount of income that is subject to tax, you know, for the donor.
Donating appreciated stock, for instance, can be very tax-efficient. The donor gets a deduction for the fair market value of the stock. They also avoid paying capital gains tax on that donated stock. It's a win-win, in some respects, for charity and the donor.
Elon Musk has made various charitable contributions through the Musk Foundation. These actions can certainly affect his overall tax picture. It's a common practice, actually, among the very wealthy.
Borrowing Against Assets
Instead of selling shares, billionaires can sometimes borrow money using their stock as collateral. This is a way to get cash without triggering a taxable event. The loan itself is not considered income, you know.
They can use this borrowed money for personal expenses or new investments. They don't pay income tax on the loan proceeds. The interest on these loans might even be deductible, depending on the circumstances, so.
This strategy allows them to maintain ownership of their valuable assets. It defers capital gains taxes until they eventually sell the stock. It's a pretty sophisticated financial move, you know, that many high-net-worth people use.
Public Perception Versus Tax Reality
There's often a big difference between what the public thinks about billionaire taxes and the actual tax laws. People might feel that the very wealthy don't pay their fair share. This feeling often comes from misunderstanding how their income is structured, you know.
The tax system is designed to tax income when it's realized. It doesn't tax wealth that's still tied up in assets. This means someone can be incredibly rich but have a low taxable income in a given year, or very little, in a way.
Discussions about "taxing the rich" often focus on wealth taxes. A wealth tax would tax assets annually, whether they are sold or not. This is a very different concept from income tax, actually, and it's not currently in place in the U.S. federal system.
It's important to separate wealth from taxable income when talking about these issues. The two are related, of course, but they are not the same thing. This distinction is pretty fundamental to understanding the whole picture.
When news reports mention Elon Musk's tax payments, they are usually referring to taxes paid on realized income. This includes income from exercising stock options. It's not about his entire net worth, you know, being taxed every year.
The tax system, as it stands, allows for deferral of taxes on unrealized gains. This is a key reason why many billionaires can appear to pay less in taxes relative to their overall wealth. It's a legal feature of the current tax code, too.
To learn more about income tax principles on our site, you can check out our other resources. We try to make these complex topics a bit easier to understand, you know.
Frequently Asked Questions About Billionaire Taxes
How do billionaires avoid paying taxes?
Billionaires don't "avoid" paying taxes in an illegal sense. They use legal strategies to minimize their tax burden. This often involves deferring taxes on unrealized gains. They also use deductions like charitable contributions. They might also borrow against their assets instead of selling them, so.
Do billionaires pay income tax on their stock gains?
Yes, billionaires pay income tax on their stock gains, but only when those gains are "realized." This means they pay tax when they actually sell the stock for a profit. They do not pay tax on the increase in value of their stocks if they haven't sold them yet, which is called an "unrealized gain," you know.
What is an unrealized gain?
An unrealized gain is the increase in the value of an asset, like a stock, that you still own. It's a gain on paper, but you haven't sold the asset yet. Because the gain isn't "realized" into cash, it's not subject to income tax until you sell it, more or less.
For more detailed information on personal finance and wealth management, you can visit a reliable financial news site, like this one: Investopedia's guide on how billionaires pay taxes. Also, feel free to link to this page for more related articles on our platform.

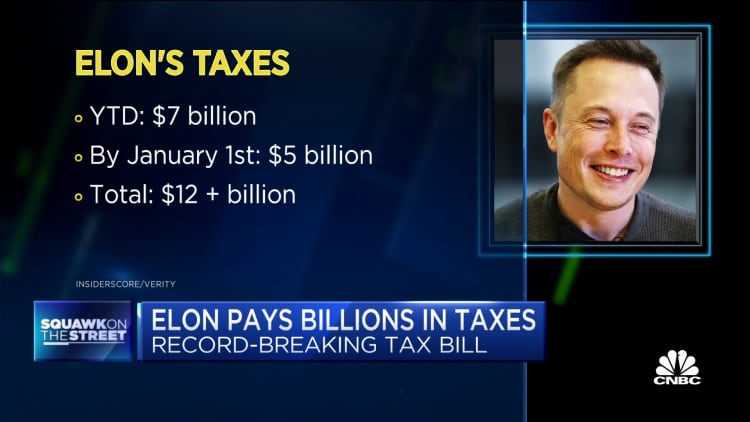
Detail Author:
- Name : Dr. Jayce Bashirian I
- Username : vcartwright
- Email : amiya63@carroll.info
- Birthdate : 2007-03-19
- Address : 716 Prohaska Camp Apt. 667 Darylfurt, TN 59224-0247
- Phone : 1-813-798-7942
- Company : Barrows Group
- Job : CTO
- Bio : Possimus quas quas at et reprehenderit. Illum sit facere animi praesentium perspiciatis. Nihil voluptatum blanditiis alias amet. Aut voluptate nemo ut animi ut quo dolores.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/norbertjast
- username : norbertjast
- bio : Enim nobis ullam totam reprehenderit aperiam et.
- followers : 399
- following : 1248
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/norbert5769
- username : norbert5769
- bio : Accusantium nihil soluta commodi eligendi. Dolores quo qui officiis quasi.
- followers : 477
- following : 698
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/jast1984
- username : jast1984
- bio : Aut dolorem et officia necessitatibus minus libero voluptatem. Ex autem cumque molestiae sequi sapiente explicabo et.
- followers : 2964
- following : 286
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/jastn
- username : jastn
- bio : Expedita inventore labore repudiandae dolores ut.
- followers : 540
- following : 368